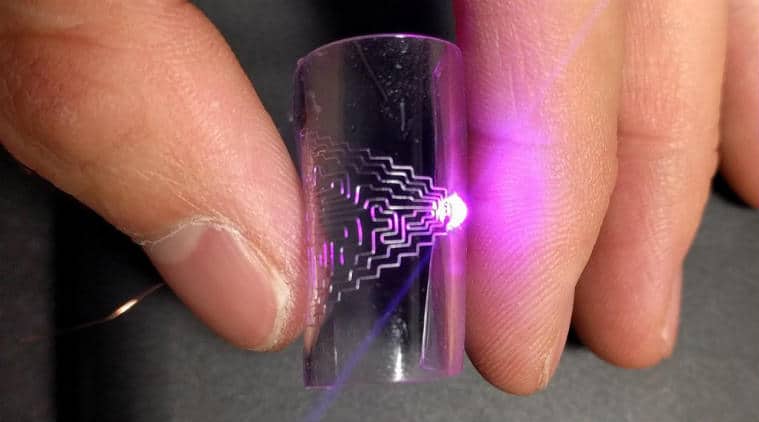
Washington: Scientists have developed a technique for directly printing metal circuits, to create flexible, stretchable electronics. The technique can use multiple metals and substrates and is compatible with existing manufacturing systems that employ direct printing technologies.
“Flexible electronics hold promise for use in many fields, but there are significant manufacturing costs involved – which poses a challenge in making them practical for commercial use,” said Jingyan Dong, from North Carolina State University in the US.
“Our approach should reduce cost and offer an efficient means of producing circuits with high resolution, making them viable for integrating into commercial devices,” Dong said. The technique uses existing electrohydrodynamic printing technology, which is already used in many manufacturing processes that use functional inks.
However, instead of ink, researchers used molten metal alloys with melting points as low as 60 degrees Celsius. The researchers have demonstrated their technique using three different alloys, printing on four different substrates: one glass, one paper and two stretchable polymers.
“This is direct printing. There is no mask, no etching and no molds, making the process much more straightforward,” said,” Dong said. The researchers tested the resilience of the circuits on a polymer substrate and found that the circuit’s conductivity was unaffected even after being bent 1,000 times. The circuits were still electrically stable even when stretched to 70 per cent of tensile strain.
The researchers also found that the circuits are capable of ‘healing’ themselves if they are broken by being bent or stretched too far. “Because of the low melting point, you can simply heat the affected area up to around 70 degrees Celsius and the metal flows back together, repairing the relevant damage,” Dong said.
The researchers demonstrated the functionality of the printing technique by creating a high-density touch sensor, fitting a 400-pixel array into one square centimetre. “We’ve demonstrated the resilience and functionality of our approach, and we’re open to working with the industry sector to implement the technique in manufacturing wearable sensors or other electronic devices,” Dong said.
PTI