Washington: A recent study has discovered the reason behind the hearing loss after we listen to loud noises or sound.
The study published in the journal ‘Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences’ explains the science behind our ears feeling numb and losing the sense of hearing temporarily.
“Most people have experienced that their hearing is impaired and the ear feels numb after listening to loud sounds. After a while hearing returns to normal. We have discovered that a tiny structure in the cochlea known as the tectorial membrane plays an important role in this process, by acting as a storage depot for calcium ions. These calcium ions contribute to regulating the function of the sensory cells”, said lead study author Anders Fridberger.
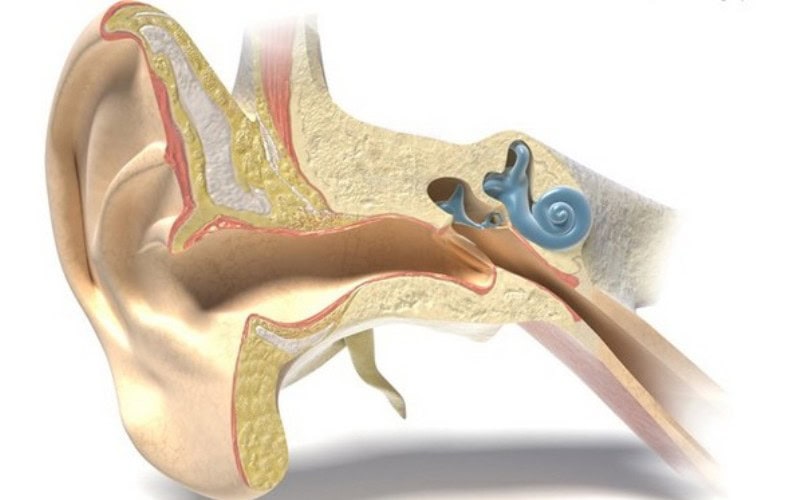
Calcium ions, which are calcium atoms with a positive charge, play a key role in the processes that make hearing possible. The conversion of sound waves to nerve impulses takes place in the inner ear, also known as the cochlea, which looks like the spiral shell that some snails have. The cochlea contains many sensory cells, which detect sounds and generate signals that are passed on to the brain.
Previous research has shown that the fluid that surrounds the sensory cells in the cochlea has a low concentration of calcium ions. There were, however, questions surrounding this, because sensory cells that are placed in fluids with the natural level of calcium no longer work normally.
When the scientists added a substance that mops up calcium ions, the sensory cells ceased to function. In the next step, they exposed the inner ear to noise levels that correspond to those experienced at rock concerts, which had the same effect.
The research group is now planning to investigate whether the same mechanism is important in age-related hearing impairment.
[source_without_link]ANI[/source_without_link]